Key Actions
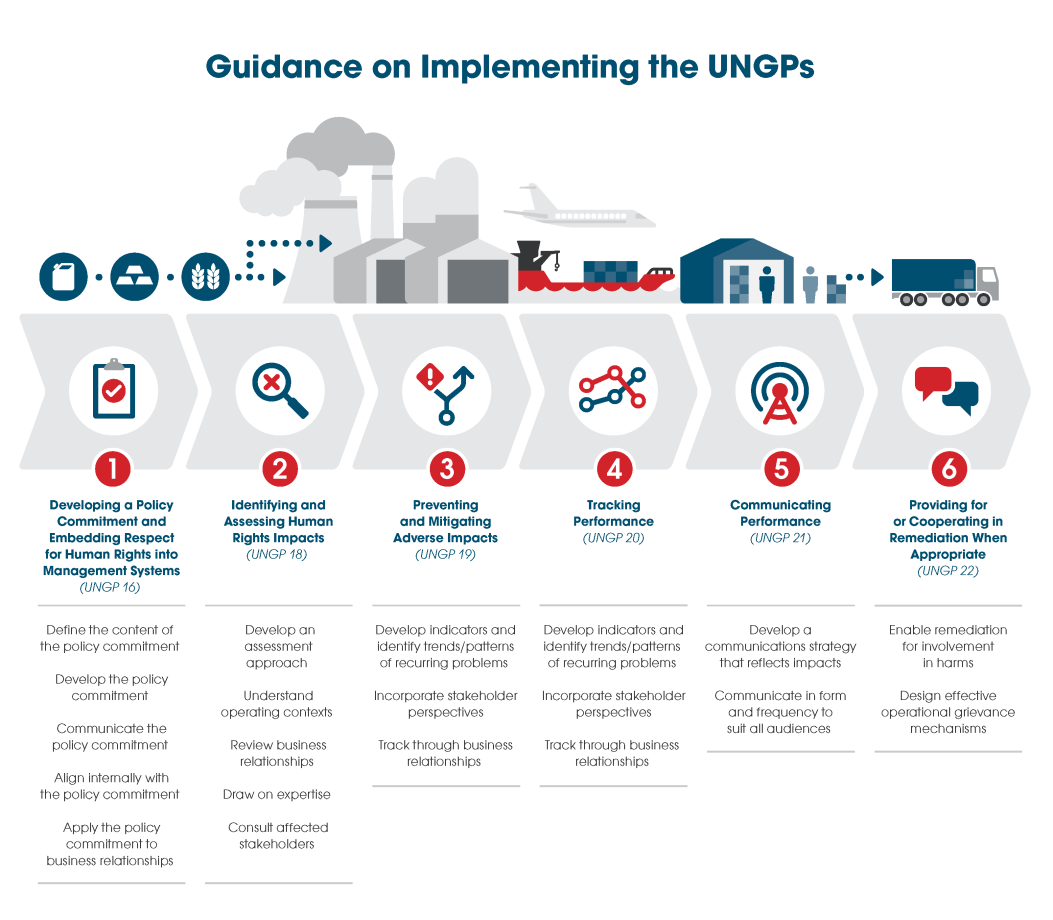
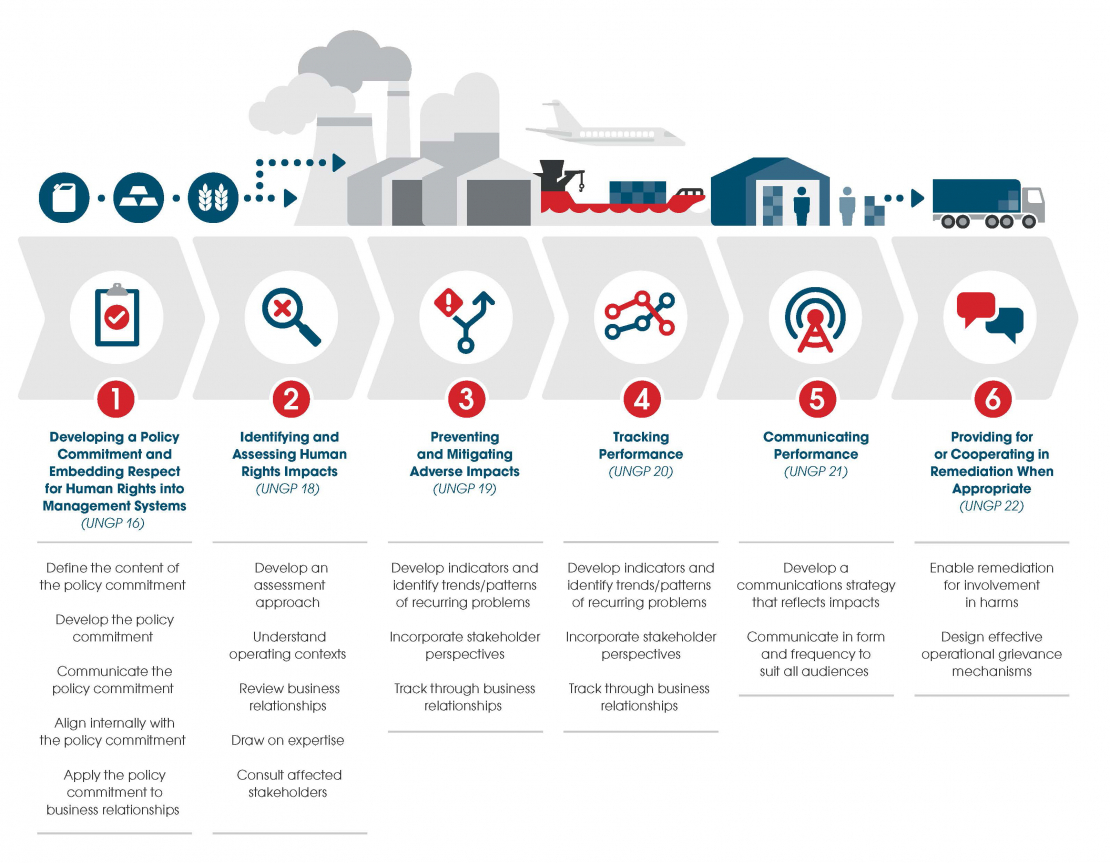
iv. Align internally with the policy commitment
The overarching policy commitment should be integrated into relevant internal policies and procedures. For example, the implications of the policy commitment should be further elaborated by other departments (e.g. Health and Safety; Security; Legal compliance and Procurement/Contracting). To be useful, the policy statement must inform the activities of all parts of the company. Regular internal discussion and reporting ensure consistency between different departments. The company should work towards coherence with other policies to ensure consistency and develop a formal process on how to respond to situations where the policy is not observed.
Thought leadership from the CEO / Board / Senior Management and trainings that involve all staff are useful means to align at different levels within the company. Oversight and responsibility for the implementation of the policy should be assigned to relevant senior management (OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Business Conduct p.23). The ultimate accountability for human rights commitments lies at senior management level and as such, it is recommended that policy commitments are formally supported by governance structures at the highest level of the organisation.
Ancillary policies and guidelines
Ancillary policies and guidelines are specific commitments which are necessary to put into action the primary human rights commitment made by the company. Such documents may specify the expectations for suppliers, commitments to transparency, guidance on remediating human rights harms, set out sector-specific expectations for business partners and other relevant parties or detail the methodology for tracking the company’s human rights impacts.
Example Ancillary policies and guidelines - types
Policy:
- High level policy on human rights applicable for the whole company
- Ancillary policies dedicated to specific topics applicable for the whole company
- Ancillary policies applicable at a specific site/office or jurisdiction (For example, a contractor procurement procedure could differ across various jurisdictions.)
Guidance documents:
- These describe how the commitments made in the policy documents are implemented by the company.
Toolkits:
- Software, databases, questionnaires, training material used for the actual implementation of the policies.
Example Ancillary policies - stakeholders
For board and employees:
- A high level policy on human rights commitments (which sets out the Board's expectations of the corporate group as a whole)
For contractors:
- A contractor procurement and screening policy (which specifies expectations and the screening criteria that contractors and third parties must meet
For suppliers and employees:
- A policy detailing grievance mechanisms (which specifies how stakeholders can promptly and safely raise any concerns about harms)
For employees and stakeholders:
- A policy which sets out expectations for suppliers regarding human rights and labour rights.