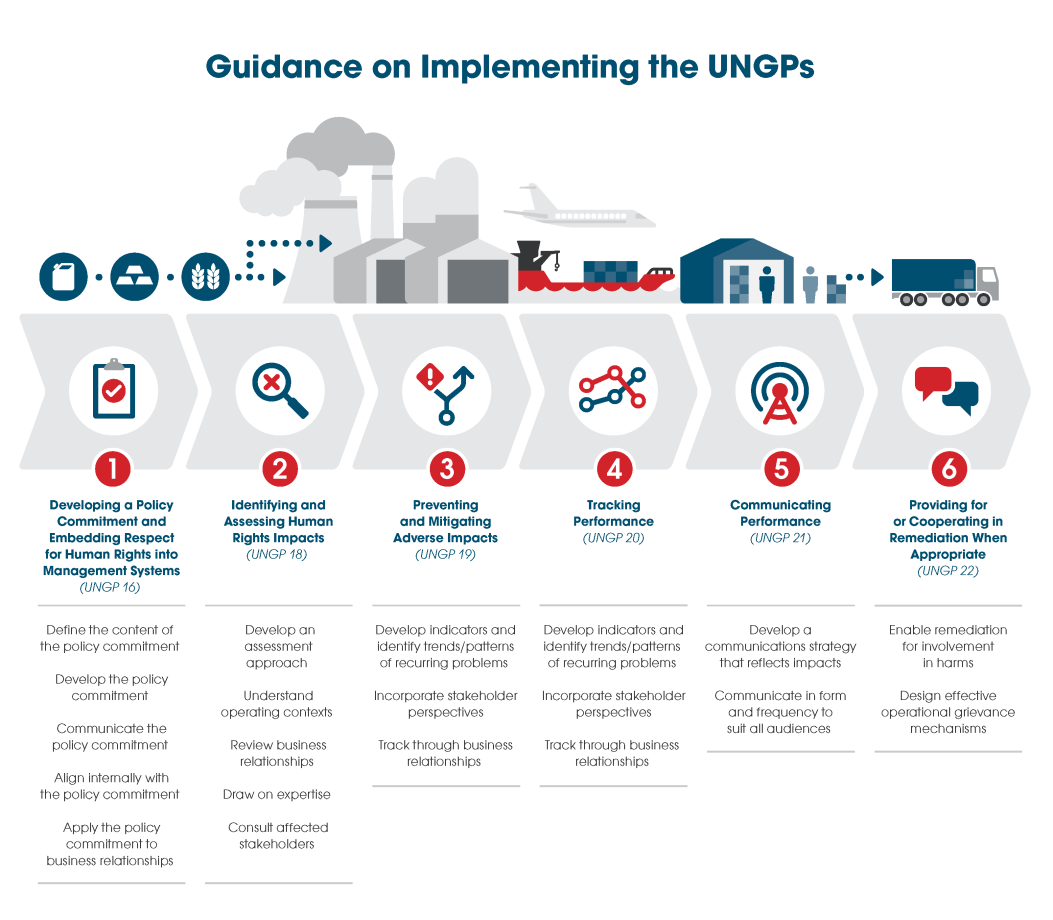
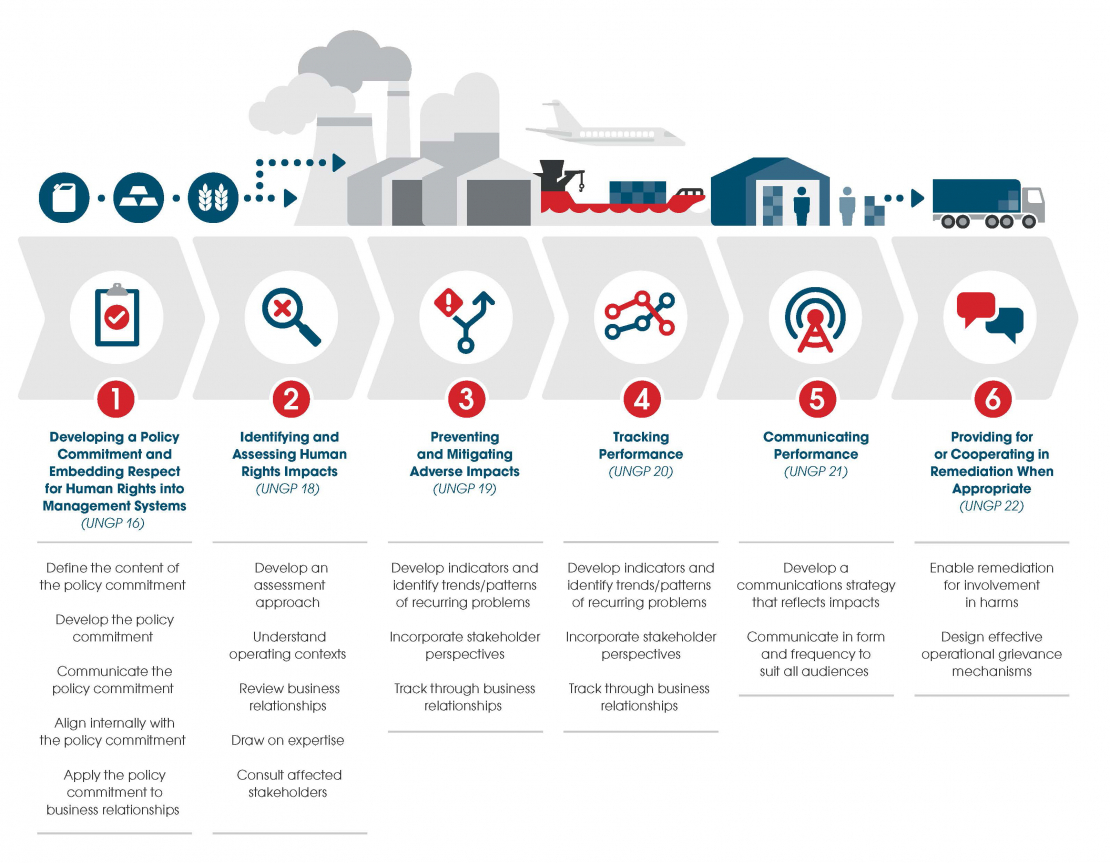
Key Actions
ii. Incorporate stakeholder perspectives
Customers, staff and affected stakeholders might have different views on how a company is managing human rights risks. Instruments to collect information from external stakeholders include:
- engagement with members of staff through workshops to identify their perspectives of risks to people across the company’s supply chain;
- collaboration with trade unions and/or NGOs locally or at the global level;
- joint fact-finding or monitoring programmes in cooperation with external experts;
- external advisory panels to provide periodic reviews of company performance;
- identification of partners that communities will trust to provide independent assessments of company efforts to address adverse impacts;
- dialogue with communities in the form of face-to-face meetings or perception or feedback surveys.
Sharing information about the tracking system and sharing information to assess a company’s implementation progress on specific commitments enables further dialogue and potential for developing collaborative approaches between the company and its stakeholders.
Customers, staff and other stakeholders can offer valuable perspectives on the effectiveness of a company’s human rights due diligence and may raise questions or concerns that would not be highlighted without such engagement. At the local level, companies may seek feedback on their human rights performance through their own internal grievance mechanisms. This could involve for example community hotlines or other anonymous complaint mechanisms through which those directly affected can raise concerns about how they are or may be harmed.